Diabetes is a serious, chronic metabolic disorder in which the body can’t metabolize carbohydrates from foods properly. For people without, sugars broken down from carbs in their diet enter cells with the help of the hormone insulin. Cells then use this sugar for energy.
In people with diabetes, they either don’t produce enough insulin or their cells have become resistant to it. Luckily, diabetes is typically manageable with diet, oral and injectable medication, and insulin. But when diabetes isn’t managed well, one of the more serious complications of diabetes is diabetic kidney disease.
Diabetes and High Blood Sugar
When blood glucose levels remain too high over time, damage to the body can occur. This includes:
- Diabetic retinopathy (eye damage)
- Diabetic kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy)
- Damage to nerves (diabetic neuropathy)
- Amputation of lower limbs
- Heart damage
Diabetes is serious. It can lead to blindness and heart failure. It can destroy the kidneys to the point of needing dialysis or a kidney transplant. The earlier in life the disease occurs, the more time it has to damage organs. Control of blood sugar levels is the best way to reduce your risk.
Diabetic Kidney Disease Symptoms
Diabetic kidney disease is one of the most serious complications that can come with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. According to the Mayo Clinic, 1 in 3 people in the US have the disease. To determine whether you may have the condition, there are some symptoms to look out for, including the following:
- Worsening blood pressure control
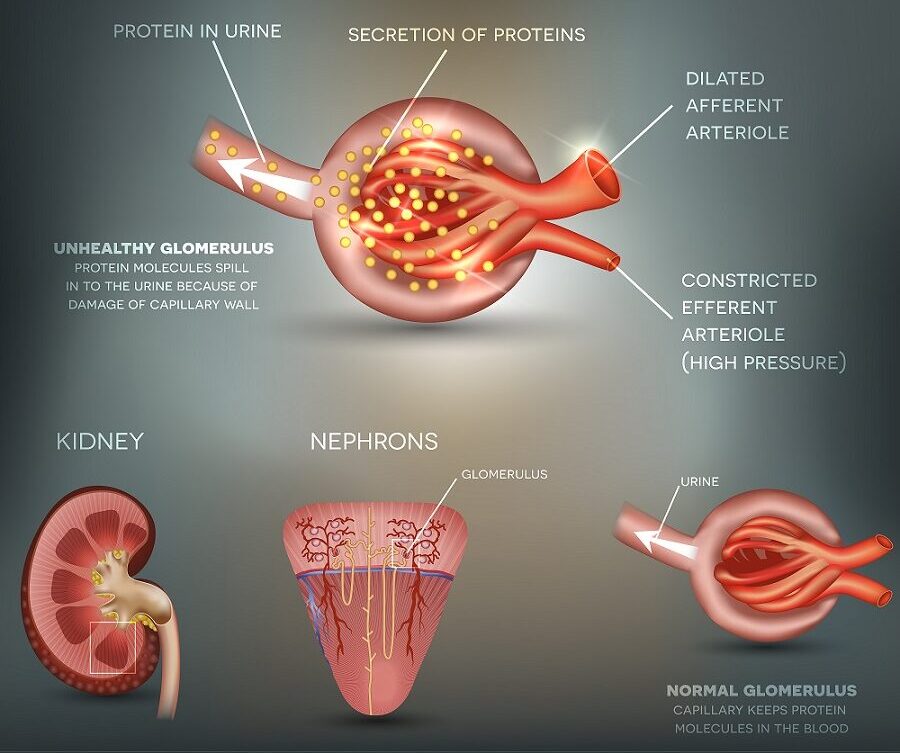
- Protein in the urine
- Swelling of feet, ankles, hands or eyes
- Increased need to urinate
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent itching
- Fatigue
Kidney Disease Can Be Silent
Unfortunately, sometimes no symptoms show up when you have kidney disease. Kidney damage can be subtle and not necessarily produce symptoms, especially at first. This is why kidney function blood tests are important. The results of these tests reveal critical information about kidney function even before symptoms appear.
Diabetic Kidney Disease Treatment
Diabetic kidney disease treatment includes keeping your diabetes under control, as well as using medications like ARBs and ACE inhibitors. These control high blood pressure and help protect the kidneys from further damage.
Other medications called SGLT2 inhibitors lower blood sugar levels and can help protect the kidneys as well. Patients may also be advised to follow a special diet plan for their diabetes and diabetic kidney disease. This may involve putting limits on how much sodium, carbs, potassium, and protein you consume.
Beyond medications, there are also a few procedures that can help treat diabetic kidney disease, including kidney dialysis and a kidney transplant. With dialysis, waste and extra fluid are removed from the blood. Normally, your kidneys would do this, but due to damage done by the disease, dialysis may be needed.
A kidney transplant is often done when the damage to the kidney is so extensive that a new kidney is the best option. Your doctor will help you determine if you are eligible for a transplant.
Schedule A Consultation At the Kidney Clinic of North Florida
Dr. Gaurav Tandon and Dr. Vishesh Puri invite you to schedule a consultation at the Kidney Clinic of North Florida if you have any symptoms or concerns about diabetes and kidney disease. It’s better to catch any kidney problems early so we can start treatment as quickly as possible.
To schedule a consultation today, call our Jacksonville, FL office at +1 904-593-5333 or use our online contact form.